Communication: Meaning, Concepts, and Principles - A Teacher's Guide
Communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction
and is crucial in personal, professional, and social contexts. This guide aims
to provide teachers with a comprehensive understanding of communication
concepts, which they can use to enhance their teaching methods and help
students develop strong communication skills.
Meaning and Concept of Communication
Communication can be defined as the process of exchanging
information, ideas, thoughts, feelings, and emotions between two or more
individuals or groups. It is a dynamic and ongoing process that involves
sending, receiving, and interpreting messages.
Examples:
- A
teacher explaining a concept to students
- Two
friends discussing their weekend plans
- A
company sending an email newsletter to its customers
- A
traffic light signalling drivers to stop or go
Principles of Communication
Several key principles guide effective communication:
- Clarity:
Messages should be concise and easy to understand. An example is using
simple language to explain complex topics to students.
- Completeness:
Provide all necessary information to avoid misunderstandings. For example,
Provide detailed instructions for a class project, including deadlines and
assessment criteria.
- Conciseness:
Convey the message using the fewest words possible without losing meaning.
Example: Writing a brief but informative email to parents about an
upcoming school event.
- Consideration:
Be mindful of the receiver's background, emotions, and viewpoint. Example:
Adapting teaching methods to suit different learning styles in the
classroom.
- Courtesy:
Maintain a polite and respectful tone in all communications. Example:
Using respectful language when addressing students, colleagues, or
parents.
- Correctness:
Ensure the accuracy of information and use appropriate language. Example:
Double-checking facts before presenting them in a lesson.
- Coherence:
Organize thoughts logically and ensure that ideas flow smoothly. Example:
Structuring a lesson plan with a clear introduction, main content, and
conclusion.
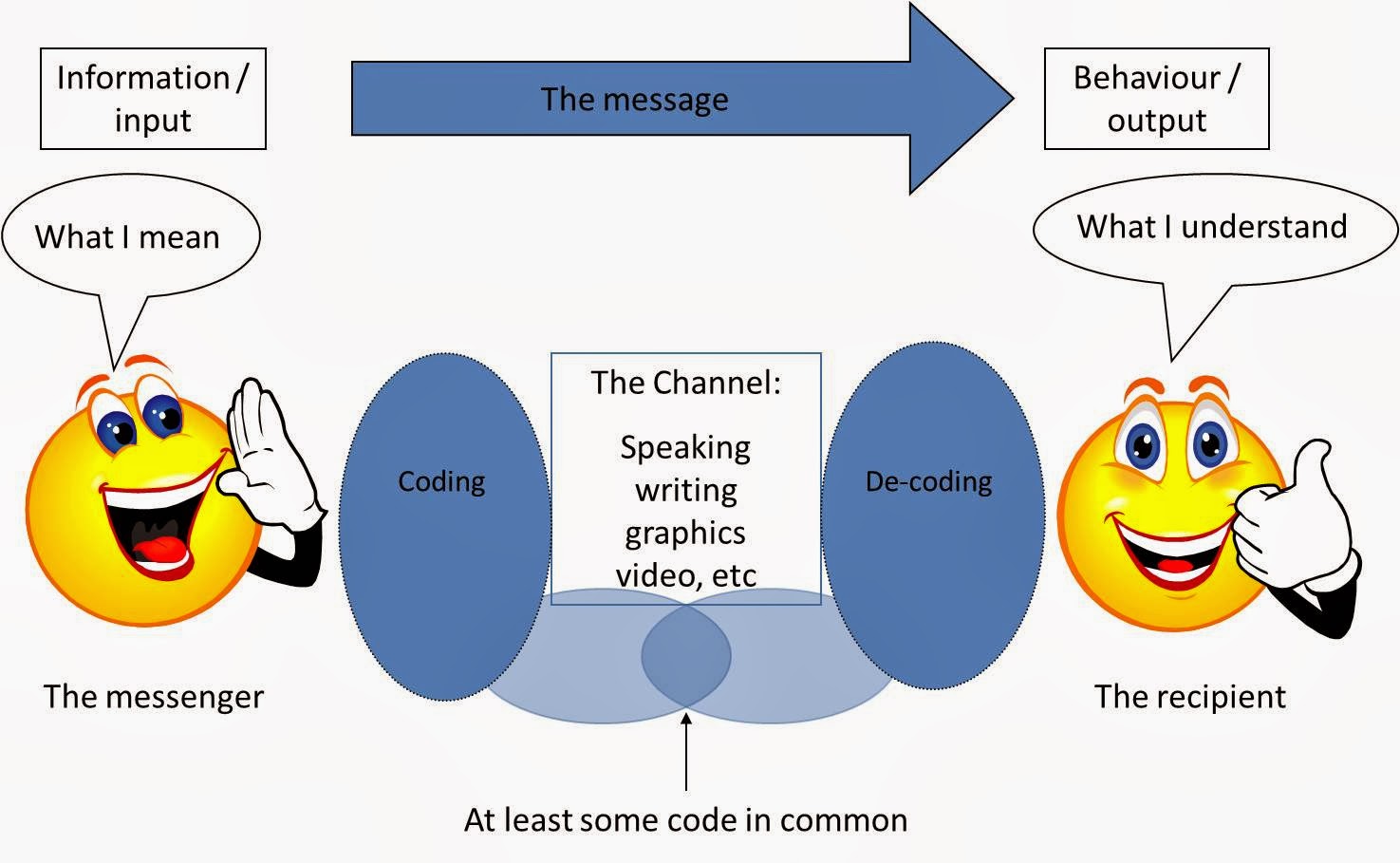
Process of Communication
The communication process typically involves the following
steps:
- Sender
(Source): The person who initiates the communication.
- Encoding:
Converting thoughts into a message (words, gestures, etc.).
- Message:
The information being communicated.
- Channel:
The medium through which the message is sent (speech, writing, etc.).
- Receiver:
The person who receives and interprets the message.
- Decoding:
Interpreting and understanding the received message.
- Feedback:
The receiver's response to the sender's message.
- Context:
The situation or environment in which the communication occurs.
Example:
A teacher (sender) wants to inform students about a test
(message). They encode this into spoken words (encoding) and announce it in
class (channel). Students (receivers) hear and understand the announcement
(decoding). They ask questions for clarification (feedback) within the
classroom setting (context).
Components of Communication
- Sender:
The originator of the message. Example: A principal addressing the school
during an assembly.
- Message:
The content being communicated. Example: A lesson on photosynthesis in a
science class.
- Medium:
The method used to transmit the message. Example: A PowerPoint
presentation used to explain historical events.
- Receiver:
The person or group receiving the message. Example: Students listening to
a guest speaker.
- Feedback:
The receiver's response or reaction to the message. Example: Students
asking questions after a lecture.
- Context:
The setting in which communication takes place. Example: A parent-teacher
conference to discuss a student's progress.
- Noise:
Any interference that disrupts the communication process. Example:
Construction sounds from outside the classroom affecting a lesson.
Benefits of Effective Communication
- Improved
Learning: Clear communication enhances students' understanding and
retention of information.
- Better
Relationships: Effective communication fosters positive relationships
between teachers, students, parents, and colleagues.
- Conflict
Resolution: Good communication skills help in addressing and resolving
conflicts more efficiently.
- Increased
Engagement: When communication is clear and engaging, students are
more likely to participate actively in class.
- Enhanced
Critical Thinking: Encouraging open communication promotes critical
thinking and discussion among students.
- Efficient
Problem-Solving: Effective communication allows for quicker
identification and resolution of problems in the educational setting.
- Cultural
Awareness: Good communication practices promote understanding and
respect for diverse perspectives and cultures.
- Professional
Development: Strong communication skills contribute to a teacher's
professional growth and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Teachers must understand the principles, processes, and
communication components to create an effective learning environment. By
mastering these concepts and applying them in daily interactions, educators can
significantly improve their teaching effectiveness and help students develop
crucial communication skills for their future personal and professional lives.


Comments
Post a Comment